ISC Computer Science Solved Question Paper 2023
ISC Computer Science Paper 2023 answer key was conducted by CISCE on March 20, 2023 and if you are looking for ISC Computer Question Paper 2023 Answer Key then you have clicked on the right link.
In this article you will get ISC Computer Solved Boards Paper 2023, also you will get solution of Section A, Section B and Section C.
Previous year solved paper are proved to be very helpful for all students as it helps students to score good marks in board exams because they are board question papers and helps a lot of students who are going to appear in board examinations.
Suggested for You:
ISC 12th Physics SOLVED Paper 2023
ISC 12th Biology SOLVED Paper 2023
ISC 12th Commerce SOLVED Paper 2023
How to Score 100 in ISC Computer Science
ISC Computer Science is one of the easiest subject among other subjects for both Commerce and Science students and you can easily score 90+ marks. If you really want some tips to score good marks in ISC Computer Science, then below are the tips shared by a topper student who score 90+ marks in ISC Computer Science.
-
Solve Boolean Algebra questions very carefully, you can
easily grab 30 marks in these questions. Always remember to write
Laws in solutions related to Boolean algebra.
-
While writing the code of Inheritance program, remember to write
extends keyword and the use of super keyword.
-
Always provide documentation i.e. comments to your code.
-
Use Buffer Reader Input instead of using
Scanner Input this will add 1 more marks in your code.
-
Don't attempt Recursion program question if you don't have
good understanding of this concept.
- Pay close attention while solving Output questions otherwise your silly mistake can make you lose some marks.
ISC Computer Science Paper 2023 Solved
Part - I (20 Marks)
(i) According to De Morgan’s law (a + b + c’)’ will be equal to:
(a) a’ + b’ + c’
(b) a’ + b’ + c
(c) a’ . b’ . c’
(d) a’ . b’ . c
(i) Option (d) is Correct,
(ii) The dual of (X’ + 1) . (Y’ + 0) = Y’ is:
(a) X . 0 + Y . 1 = Y
(b) X’ . 1 + Y’ . 0 = Y’
(c) X’ . 0 + Y’ . 1 = Y’
(d) (X’ + 0) + (Y’ + 1) = Y’
(ii) Option (c) is correct
(iii) The reduced expression of the Boolean function F(P, Q) = P’ + PQ is:
(a) P’ + Q
(b) P
(c) P’
(d) P + Q
(iii) Option (a) is correct
(iv) If (~p => ~q) then its contra positive will be:
(a) p => q
(b) q => p
(c) ~q => p
(d) ~p => q
(iv) Option (b) is correct
(v) The keyword that allows multi-level inheritance in Java programming is:
(a) implements
(b) super
(c) extends
(d) this
(v) Option (c) is correct
(vi) Write the min term of F(A, B, C, D) when A = 1, B = 0, C = 0 and D = 1.
(vi) A.B’.C’.D (Find any min term we have to find the SOP expression for variables. Here A=1, B=0, C=0, D=1 so to find the min term we have to change 0 to 1. To achieve this use the complements of B and C)
(vii) Verify if (A + A’)’ is a Tautology, Contradiction, or a Contingency
(vii) (A + A’)’ = A’.A’’ = A’.A = 0 Hence, it is a contradiction. The truth table of the above expression is:
(ix) Mention any two properties of the data members of an Interface.
(ix) Two properties are:
(a) Data members of an Interface are always declared with final keyword.
(b) Data members of an Interface cannot be changed in the due course of the program.
(x) What is the importance of the reference part in a Linked List?
(x) Reference part in a Linked List holds the address of the next node in the Linked List.
Question 2
(i) Convert the following infix notation to prefix notation.
(A – B)/C*(D + E)
(i) Prefix of the (A–B)/C*(D+E) :
(A–B)/C*(D+E)
=(–AB)/C*(+DE)
=(/–ABC)*(+DE)
=*/–ABC+DE
(ii) A matrix M[–6...10m 4...15] is stored in the memory with each element requiring 4 bytes of storage. If the base address is 1025, find the address of M[4][8] when the matrix is stored in Column Major Wise.
(ii) A = B + W( (I – I0) + (J – J0) × R)
B = 1025
W = 4
I, J = 4, 8
I0, J0 = –6, 4
R = 10 + 6 + 1 = 17
A = 1025 + 4 × ((4 + 6) + (8 – 4) × 17)
= 1025 + 4 × (10 + 68)
= 1025 + 312
= 1337
(iii) With reference to the code given below, answer the questions that follow along with dry run/working.
boolean num(int x)
{ int a=1;
for(int c=x; c>0’c/=10) a*=10;
return(x*x%a)=x; }
(a) What will the function num() return when the value of x = 25?
(b) What is the method num() performing?
(iii)
(a) X = 25 A = 1
C = 25 ® a = a * 10 = 10 ® c = 25 10 = 2
C = 2 ® a = a * 10 = 100 ® c = 2 10 = 0
X * X = 25 * 25 = 625 ® 625%100 = 25 ® true
(b) Checking whether the number x is Automorphic Number or not.
Checking whether the number x is present in its square or not.
(iv) The following function task() is a part of some class. Assume ‘m’ and ‘n’ are positive integers, greater than 0. Answer the questions given below along with dry run/working.
int task(int m, int n)
{if(m==n)
return m;
else if(m>n)
return task(m–n,n);
else return task(m,n–m); }
(a) What will the function task() return when the value of m = 30 and n = 45? 2
(b) What function does task() perform, apart from recursion?
(iv)
(a) task(30, 45) → task(30, 5) → task(25, 5) → task(20, 5) → task(15, 5) → task(10, 5) → task(5, 5) → 5
(b) Returning the HCF of two numbers, m and n.
ISC Computer Paper 2023 Solved Section A
SECTION - A
Question 3
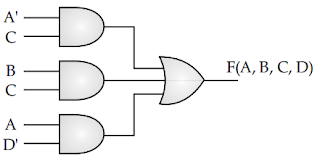
(i) Given the Boolean function F(A, B, C, D) = S(2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14, 15).
(a) Reduce the above expression by using 4-variable Karnaugh map, showing the various groups (i.e., octal, quads and pairs).
(b) Draw the logic gate diagram for the reduced expression. Assume that the variables and their complements are available as inputs.
(ii) Given the Boolean function F(A, B, C, D) = p(0, 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 11, 14, 15).
(a) Reduce the above expression by using 4-variable Karnaugh map, showing the various groups (i.e., octal, quads and pairs).
(b) Draw the logic gate diagram for the reduced expression. Assume that the variables and their complements are available as inputs.
(i) F(A, B, C, D) = ∑(2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14, 15)
(a)
= ∏(0, 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 12, 13)
(ii)
Boolean expression of Full Adder:
SUM = A ⊕ B ⊕ C
CARRY = (A ⊕ B ).C + AB
(iii)
Hence, proved (A ⊙B)’ = A ⊕ B
Question 5
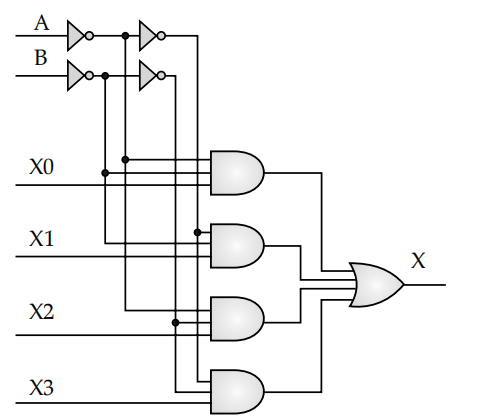
(i) What is an encoder? How is it different from a decoder? Draw the logic circuit for a 4 : 1 multiplexer and explain its working.
(ii) Form the logic diagram given below, write the Boolean expression for (1) and (2). Also, derive the Boolean expression (F) and simplify it.
(iii) Convert the following cardinal expression to its canonical form: F(P, Q, R) = p(0, 1, 3, 4)
5. (i) Encoder is sequential circuit that converts decimal/octal/hexadecimal digit to its equivalent binary form. Decoder is a circuit that does the opposite of Encoder i.e. Binary to the other form.
Logic circuit of 4 : 1 multiplexer
(ii)
Gate (1) = (x. y)’
Gate (2) = (y + z)’
F(x, y, z) = (x. y)’ + (y + z)’
(iii) F(P, Q, R) = (P + Q + R).(P + Q + R’).(P + Q’ + R’).(P’ + Q + R)
ISC Computer Paper 2023 Solved Section B
SECTION - B
Question 6
Design a class NumDude to check if a given number is a Dudeney number or not.
(A Dudeney number is a positive integer that is a perfect cube, such that the sum of its digits is equal to the cube root of the number.) Example: 5832 = (5 + 8 + 3 + 2)³ = (18)³ = 5832.
Specify the class NumDude giving details of the constructor(), void input(), int sumDigits(int) and void is Dude(). Define a main() function to create an object and call the functions accordingly to enable the task.
6.
import java.util.Scanner;
class NumDude {
int num;
public NumDude() {
num=0; }
public void input() {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter a no”);
num=sc.nextInt(); }
public int sumDigits(int x) {
if(x==0)
return 0;
else return x%10+sumDigits(x/10); }
public void isDude() {
int n=sumDigits(num);
if(n*n*n==num)
System.out.println(“Dudeney number”);
else
System.out.println(“Not a Dudeney number”); }
public static void main(String args[]) {
NumDude obj=new NumDude();
obj.input(); obj.isDude();
}
}
Question 7
A class Trans is defined to find the transpose of a square matrix. A transpose of a matrix is obtained by interchanging the elements of the rows and columns.
Example: If size of the matrix = 3, then
Specify the class Trans giving details of the constructor(), void fillarray(), void transpose() and void display(). Define a main() function to create an object and call the functions accordingly to enable the task.
ISC Computer Paper 2023 Solved Section C
(ii)
(a) A F D G B H E
(b) F and A
(c) Level of E = 3 and level of F =1
If you found this site helpful, then leave a comment below
and share your queries also. Share it with your friends
because SHARING IS CARING.



















0 Comments
Just comment your queries, we will reply as soon as possible.