ISC Physics Question Paper Answer Key 2023
ISC Physics Paper 2023 was conducted by CISCE on March 20, 2023 and if you are looking for ISC Physics Question Paper 2023 Answer Key then you have clicked on the right link.
In this article you will get ISC Physics Solved Question Paper 2023, also you will get solution of Section A, Section B, Section C and Section D.
Previous year solved paper are proved to be very helpful for all students as it helps students to score good marks in board exams because they are board question papers and helps a lot of students who are going to appear in board examinations.
Also Read:
ISC Physics Paper Answer Key 2023
SECTION - A
(i) A hollow sphere of radius R has a point charge Q at its centre. Electric flux emanating from it is j. If both the
charge and the radius of the sphere be doubled, electric flux emanating from the sphere will:
(a) remain the same.
(b) become 2φ
(c) become 4φ
(d) become 8φ
(i) Option (b) is correct.
(ii) An electric current (I) flowing through a metallic wire is gradually increased. The graph of heating power (P)
developed in it versus the current (I) is:
(ii) Option (a) is correct.
(iii) A circular coil has radius ‘r’, number of turn ‘N’ and carried a current ‘I’. Magnetic flux density ‘B’ at its centre
is:
(iii) Option (b) is correct.
(iv) If an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm, the image formed
will be:
(a) real and 20 cm in front of the mirror.
(b) real and 6.67 cm in front of the mirror.
(c) virtual and 20 cm behind the mirror.
(d) virtual and 6.67 cm behind the mirror.
(iv) Option (c) is correct.
(v) What type of wavefronts are associated with a source at infinity?
(a) Cylindrical wavefronts
(b) Plane wavefronts
(c) Spherical wavefronts
(d) All types of wavefronts
(v) Option (b) is correct.
(vi) Matter waves are:
(a) waves associated with moving particles.
(b) waves associated with stationary particles.
(c) waves associated with any charged particles.
(d) waves associated with electrons only.
(vi) Option (a) is correct.
(vii) With an increase in the temperature, electrical conductivity of a semiconductor:
(a) decreases.
(b) increases.
(c) does not change.
(d) first increases and then decreases.
(vii) Option (b) is correct.
(B) Answer the following questions briefly.
(i) What is meant by an equipotential surface?
(i) The surface where all the points are at same electric potential is said to be an equipotential surface. Since
the charge experiences same potential energy throughout the equipotential surface, the work done to take a
charge from one point to another remains zero.
(ii) In case of metals, what is the relation between current density (J), electrical conductivity (s) and electric field
intensity (E)?
(ii) For a conductor,
J = σE
where, J is the current density
σ is the conductivity
E is the electric field.
(iii) What is meant by “Motional emf”?
(iii) Motional emf (e) is the emf generated in a conductor because of its motion in a region having magnetic field B.
e = vBl
where, v is the velocity with which conductor is moving (perpendicular to length l)
B is the intensity of magnetic field
l is the length of the conductor.
(iv) What is meant by a microscope in normal use?
(iv) Microscope is a laboratory instrument used to produce enlarged images of the small objects. With the help of
microscope one can see tiny objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye.
(v) In a single slit Fraunhofer diffraction experiment, how does the angular width of central maximum change
when the slit width is increased?
(v) The angular width of the central maxima in Fraunhofer diffraction will decrease when the slit width is
increased
The angular width is given by
2 sinθ = 2λ/b
Where b is the slit width.
(vi) Name the type of nuclear reaction that takes place in the core of the Sun.
(vi) In the core of the sun, the hydrogen gets converted to helium by the nuclear reaction process called nuclear
fusion.
(vii) What type of semiconductor is obtained when a crystal of silicon is doped with a trivalent element?
(vii) When a pure Si is doped with trivalent impurity, we get p-type semiconductor due to deficiency of electron.
Holes will be the charge carriers in the case of trivalent impurity doping.
SECTION - B
Question 2
(i) Calculate equivalent capacitance of the circuit shown in Figure given below:
OR
(ii) Calculate electric potential at a point P which is at a distance of 9 cm from a point charge of 50µC.
(i) In the given figure two capacitors C₁ and C₂ are connected parallelly.
C₁= 50 µC
C₂ = 50 µC
Thus, net capacitance ‘C’ can be calculated using the formula.
C = C₁ + C₂
C = 50 + 50 = 100
Thus, net capacitance C = 100µC
This, net capacitance C is connected in series with C3. Thus, equivalent capacitance can be calculated using the
formula.
This equivalent capacitance of the circuit = 20 µC
(ii) The electric potential at point P because of charge q is given by
V = Kq/x
where, K = 1/4πε₀ = 9 × 10⁹ and x is the distance in meter from the point charge.
From the question
Thus, the potential
Question 3
(i) Write balancing condition of a Wheatstone bridge.
(ii) Current ‘I’ flowing through a metallic wire is related to drift speed vd of free electrons as follows:
I = nAevd
State what the symbol ‘n’ stands for.
(i) The balancing condition of wheatstone bridge is:
P/Q = R/S
(ii) The formula I = neAVd stands for the current flowing through the conductor. Here n stands for the number
density of free electrons (charge carriers) present in the conductor.
Question 4
When an electric current is passed through a wire or a coil, a magnetic field is produced. Is the reverse phenomenon
possible i.e., can a magnetic field produce an electric current? Explain with the help of an appropriate example.
Answer 4
Yes, the reverse phenomenon is also possible. That is, the magnetic field is also capable to produce electric current
in the circuit, just like the current flowing through the coil produces magnetic field.
For example,
Consider a circular metallic wire connected to a galvanometer. When a bar magnet is moved in and out of the coil,
there will be a generation of magnetic field. At the same time one can see a deflection in the galvanometer as well.
This is because of the current produced in the circular metallic wire as a result of magnetic field produced.
Question 5
(i) A long straight wire AB carries a current of 5A. P is a proton travelling with a velocity of 2 × 106
m/s, parallel to
the wire, 0.2 m from it and in a direction opposite to the current, as shown in Figure 2 below.
Calculate the force
which magnetic field of the current carrying conductor AB exerts on the proton.
OR
(ii) A moving coil galvanometer of resistance 55 Ω produces a full scale deflection for a current of 250 mA. How will
you convert it into an ammeter having a range of 0 – 3A?
Answer 5
(i) The magnetic field produced by the long straight wire is given.
Magnitude of force acting,
Both the currents are in same direction. So, the force on proton will be repulsive and it will be towards right
i.e. away from the current carrying wire.
(ii) Given, the resistance of galvanometer G = 55 Ω
The current for which, full scale deflection is observed in the galvanometer, i = 250 mA.
Range of ammeter is thus 250 mA which needs to be converted to 3A Thus, I = 3A
In order to convert the moving coil galvanometer into ammeter in the range of 0-3A, we need to connect a a
shunt S parallel to the galvanometer.
The value of S can be obtained using the equation
Question 6
(i) State how vectors →E →B, and →c are oriented in an electromagnetic wave.
(ii) Name the electromagnetic wave/radiation which is used to study crystal structure.
Answer 6
(i) The electric vector →E, the magnetic vector →B and the velocity vector →c are mutually perpendicular to each
other.
(ii) X-rays whose frequency lies in the range of 10¹⁷ Hz to 10¹⁹ Hz is used to analyse the crystal structure.
Question 7
Name any two phenomena which take place in the formation of a rainbow.
Answer 7
The phenomenon such as total internal reflection and dispersion are responsible for the formation of rainbow.
Question 8
With reference to semiconductor physics, answer the following questions.
(i) What is meant by “Forbidden band” of energy levels?
(ii) In which material “Forbidden band” is absent?
Answer 8
(i) The difference between the top most energy level of valence band and bottom level of conduction band is
called forbidden band energy. This forbidden energy gap usually lies in the range of few eV.
(ii) The forbidden band is absent in the case of metals. In this case, there is overlapping between the valence band
and the conduction band leaving no energy gap between them.
SECTION - C
Question 9
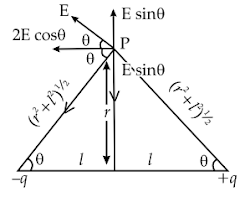
Show that intensity of electric field at a point in broadside position of an electric dipole is given by:
Where the terms have their usual meaning.
Answer 9
Consider a point P at on broadside position of an electric dipole having a distance of ‘r’ meter from the middle
point of the dipole. The length of the dipole be 2l.
Let E1 be the electric field intensity generated at P due to +q and E2 be the electric field generated at point P due
to –q. From the figure using Pythagoras theorem, the distance to point P from each charge of dipole is given as .
The intensity of Electric Field E1 due to
The intensity of the Electric Field E2 due to
The magnitude of E1 and E2 are equal.
On resolving E1 and E2 the components perpendicular to the dipole gets cancel while the components parallel to
the dipole AB gets added up.
That is, the component E1 sinθ and E2 sinθ cancel each other because of their opposite direction while the
components E1 cosθ and E2 cosθ are added up since they are in same direction.
Thus, net electric field E at the point P = E1 cosθ + E2 cosθ
From the Figure
Since 2ql = p(dipole moment)
Net Electric Field at point P =
Hence, proved
Question 10
(i) Eight identical cells, each of emf 2V and internal resistance 3W, are connected in series to form a row. Six such
rows are connected in parallel to form a battery. This battery is now connected to an external resistor R of
resistance 6W.
Calculate:
(a) emf of the battery.
(b) internal resistance of the battery.
(c) current flowing through R.
OR
(ii) In the circuit shown in Figure below, E₁ and E₂ are batteries having emfs of 25V and 26V. They have an internal
resistance of 1W and 5W respectively. Applying Kirchhoff’s laws of electrical networks, calculate the currents I₁ and I₂.
Answer 10
(i) (a) The emf of each row is
E = 8 × 2 = 16V
Equivalent emf of the combination,
Eeq = 16V
(b) Internal resistance of each row = 3 × 8 = 24Ω
6 such rows are in parallel.
If req is the equivalent internal resistance of the battery, then
(c) From part (b) solution, total internal resistance, req = 4Ω.
When the battery is connected to an external resistance R = 6Ω then the total resistance of the circuit = req + R
= 4Ω + 6Ω =10Ω
Now, the current flowing through external resistance R can be obtained using Ohm’s law V = IR
(ii)
In loop HJBAFEGH
26 – 5I2 – 3I2 + 4I1 + 1 × I1 – 25= 0
Or, 8I2 – 5I1 = 1 ….(1)
In loop ABCDEFA
2(I1+ I2) + 3I2 + 5I2 – 26 = 0
Or, I1 + 5I2 = 13 ….(2)
Solving (1) and (2)
I1 = 3A
I2 = 2A
Question 11
Using Ampere’s circuital law, obtain an expression for magnetic flux density ‘B’ at a point near an infinitely long
and straight conductor, carrying a current I.
Answer 11
According to amperes circuital law, the “line integral of the magnetic field surrounding closed-loop equals to the
number of times the algebraic sum of currents passing through the loop”.
Thus mathematically, it can be expressed as
Considering the small elemental length of the straight wire, we have ∮dl = 2πr
Where r is the radius of the wire.
Now, B.2πr = µ0I where ∑i = I(total current in the circuit)
Thus, the intensity of magnetic flux density B at a point near infinitesimally long straight wire can be given as.
Question 12
Using Huygen’s wave theory of light, show that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Draw a
neat and labelled diagram.
Answer 12
Huygens principle states that each point of a wave acts as a source for secondary wave fronts.
In order, to prove the laws of reflection
With reference to the figure shown below,
Let us consider that,
MN be the reflecting side of the mirror.
Consider a wave front AB incident on MN side of the mirror
i be the angle of incidence
r be the angle of reflection
Let τ be the time taken by the wave front to travel from the point B to C, then distance BC = vτ
The reflected wave front can be constructed by drawing a sphere of radius vτ and centre A as shown in the figure.
Let CE represents the tangent plane drawn from the point C to this sphere. Then AE = BC = vτ,
Considering triangle EAC, and BAC
ÐABC = ÐCEA = 90° and AC is common side.
The triangle EAC and BAC are congruent.
Thus, i = r
Hence the laws of reflection that angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection is proved by Huygens principle
Question 13
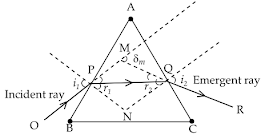
(i) For any prism, obtain a relation between angle of the prism (A), angle of minimum deviation (dm) and refractive
index of its material (m or n).
OR
(ii) Obtain an expression for refraction at a single convex spherical surface i.e, the relation between m1 (rarer
medium), m2 (denser medium), object distance u, image distance n and the radius of curvature R.
Answer 13
(i) With reference to the figure,
OP is the incidence ray, which is making the angle i1, with the normal, and QR is the emergent ray which
makes angle i2 with the normal.
Let A and n be the angle of prism and refractive index respectively.
In the case of minimum deviation, 
The angle 
Thus 
Also,
However, for minimum deviation we have,

According to snell’s law, the refractive index of a medium

Thus,
Hence the relation between angle of incidence, angle of minimum deviation and refractive index of the
material is obtained.
OR
(ii) Let the object be kept at a point O in the rarer medium of refractive index m1.
The image of the object is formed at I as a result of refraction of convex spherical surface in another medium
having refractive index m2.
Consider that the convex surface have small aperture.

From the figure,
Now a perpendicular AN is drawn to the principal axis
By Snell's Law,
Since i and r are small
We have µ₁i = µ₂r
From triangle AOC, i = α + γ
From triangle IAC, r = γ – β
Thus,
Since α, β and γ are small, their tangents can be taken.
Since the lens has small aperture, N lies close to P
Thus, NO = OP = –u
NI = IP = v
NC = R
Thus, we can obtain the equation,
Question 14
(i) What is the essential condition for obtaining a sustained interference?
(ii) In Young’s double slit experiment, the distance of the 4th bright fringe from the centre of the interference pattern
is 1.5 mm. The distance between the slits and the screen is 1.5 m and the wavelength of light used is 500 nm.
Calculate the distance between the two slits.
Answer 14
(i) There exists several conditions under which one can obtain a sustained interference pattern. They are
1. The two light sources must be coherent with same frequency, same wavelength, same phase or with constant
phase difference.
2. The two sources must be very close to each other with almost same amplitude.
3. The light source should emit the waves continuously without any delay.
(ii) The distance of nth bright fringe from the central maxima of interference pattern is given by
Where λ is the wavelength of light used
D is the distance of screen from the slits
d is the distance between slits
Given,

Since, 
Therefore, the distance between the slits is 2 mm.
Question 15
Monochromatic light of wavelength 396 nm is incident on the surface of a metal whose work function is 1.125 eV.
Calculate:
(i) the energy of an incident photon in eV.
(ii) the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons in eV.
Answer 15
(i) The energy of incident light E = hc/λ
(ii) The energy E = Work function (W0) + Kinetic Energy (Ek)
The Kinetic energy Ek = E – W0
Ek = E – W0 = 3.43 – 1.125 = 2.305 eV
Question 16
Name any two essential parts of a nuclear reactor. State the function of any one of them.
Answer 16
Two essential parts of a nuclear reactor are coolants and the moderator.
The function of coolant in the nuclear reactor is to remove the enormous amount of heat produced in the core
of the reactor during the nuclear reaction process and to transfer them to the electrical generators. There exist
gaseous coolants as well as liquid coolants.
Question 17
Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a full wave rectifier. Show graphically how the output voltage varies with
time.
Answer 17
SECTION-D
Question 18
(i) A 60 ohm resistor, a 1.0 H inductor and a 4 mF capacitor are connected in series to an ac supply generating an emf e =
300 sin (500t) V. Calculate:
(a) impedance of the circuit.
(b) peak value of the current flowing through the circuit.
(c) phase difference between the current and the supply voltage.
Answer 18
(i) (a) In the case of LCR circuit the Impedence
Given,
R= 60 ohm
L= 1 H
C = 4 µF
The emf,
Similarly,
Hence, Impedence,
(b) Peak Current I₀ = V/Z₀
The peak value of voltage ,
V₀ = 300√2 = 424.3 V
Hence, I₀0 = 424.3/60 = 7.07 A
(c) The phase difference is given by tanɸ = Xı - Xc / R
Since Xı - Xc, there is no phase difference between the current and the supply voltage.
The current is in phase with the voltage.
(ii)
(a) An ac generator generates an emf which is given by e = 311 sin(240πt)V. Calculate:
(1) frequency of the emf.
(2) r.m.s. value of the emf.
(b) The primary coil of a transformer has 60 turns whereas its secondary coil has 3000 turns.
(1) If a 220V ac voltage is applied to the primary coil, how much emf is induced in the secondary coil?
(2) If a current of 5A flows in the primary coil, how much current will flow in a load in the secondary coil?
State the assumption you have made regarding the transformer, in this calculation.
OR
(ii)
(a) Given, e = 311 sin(240π)t
Thus ω = 240π
We also have ω = 2πf.
(1) Thus, frequency,
f = ω/2π = 240π/2π = 120 Hz
(2) The rms voltage can be written as,
(b) We know that for a transformer
Where,
Es and Ep are the emf is the secondary and primary coil respectively.
Ns and Np are number of turns in the secondary and primary coil respective ly.
Ip and Is are the currents
in primary and secondary coil respectively.
Question 19
(i)
(a) Name the series of lines of hydrogen spectrum which lies in the (1) ultraviolet region.
(2) visible region.
(b) How much is the angular momentum of an electron when it is orbiting in the second Bohr orbit of hydrogen
atom?
(c) With reference to Nuclear Physics, answer the following questions.
(1) What is meant by “Isotopes”?
(2) Define 1u(where u stands for unified atomic mass unit).
Answer 19
(i) (a)
1. Lyman Series of hydrogen spectrum lies in UV region. The transition of electron from n ≥ 2 to n = 1
results in the formation of Lyman series where n is the principle quantum number.
2. Balmer Series of hydrogen spectrum lies in visible region. The transition of electron from n ≥ 3 to n = 2
results in the formation of Balmer series where n is the principle quantum number.
(b) The angular momentum L is given by nh/2π . For the electron orbiting in second Bohr orbit, the value of n is
2.
Thus, L = 2h/2π = h/π.
(c)
1. The atoms those have equal number of protons but different number of neutrons are called isotopes.
They generally have same atomic number and different mass number.
An example is C12
6 and C14
6 . Here, the carbon C has same atomic number 6 while their mass numbers are
different.
2. 1u is equal to the unit of mass equal to 1/12th of the mass of one atom of C12 isotope. 1u can also be defined
as 1 atomic mass unit (1 amu).
OR
(ii) (a) Using Bohr’s Theory of hydrogen atom, obtain an expression for the velocity of an electron in nth orbit of an
atom.
(b) What is meant by “binding energy per nucleon” of a nucleus? State its physical significance.
(ii) (a) The necessary centripetal force required for the electron to revolve around the nucleus is provided by the
electrostatic force between the electron and the nucleus.
Thus, by equating both the forces we have
Where,
Z = atomic number
r = radius of the orbit
m = mass of the electron
Also,
We have, the angular momentum L = nh/2π
i.e., mvr = nh/2π ...(ii)
Divide the equation (i) by (ii) we have,
Thus, the velocity of electron in the nth orbit is given by
Velocity of the electron is directly proportional to atomic number z and inversely proportional to principal
quantum number n.
(b) Binding energy (B.E) per nucleon is the minimum amount of energy needed to remove a nucleon from the
nucleus. Stability of the element can be estimated from the value of Binding Energy per nucleon.
One has
to do more work to separate a proton or neutron from the nucleus of an atom with higher binding energy
per nucleon. The average B.E per nucleon will always be in the range of MeV.
Question 20
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow.
There are two types of lenses: Converging lenses and Diverging lenses, depending on whether they converge or
diverge an incident beam of light. They are also called convex or concave lenses. Lenses are usually made of glass.
Convex lenses are more popular as they form a real image of an object. They are widely used in our daily life, for
instance, in microscopes, telescopes, projectors, cameras, spectacles etc. Microscopes are used to view small and
nearby objects whereas telescopes are used to see distant objects.
(i) State any one factor on which focal length of a lens depends.
(ii) Give an example where a convex lens behaves like a diverging lens.
(iii) What type of lens is used in a camera?
(iv) Write an expression for magnifying power of a compound microscope when its final image lies at the least
distance of distinct vision (D).
(v) State any one difference between reflecting telescope and a refracting telescope.
Useful Constants & Relations:
Answer 20
(i) Focal length of lens depends on, the radius of curvature of the lens.
(ii) The convex lens gives divergent rays when it is placed in a medium whose refractive index is higher than that
of lens. For example, the convex lens with refractive index 1.525 when placed in carbon disulphate having
higher refractive index of 1.6 behaves as diverging lens.
(iii) Normally, a standard lens whose focal length lies in the range of 3.5 cm to 8 cm is used in cameras. Such lenses
are supposed to give a field of view similar to that of a human eye.
(iv) The magnifying power M of compound microscope is generally given as.
(v) The major difference between reflecting and refracting telescope lies in the material with which they are made
up of. That is, in the case of reflecting telescopes mirrors are used while in the case of refracting telescopes
lenses are used.
Reflecting telescopes is in size than the refracting telescopes and they suffer only less aberrations compared to
that of refracting ones. Refracting telescopes are heavier than reflecting telescopes.
If you found this site helpful, then leave a comment below and share your queries also. Share it with your friends because SHARING IS CARING.







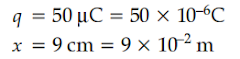














































.png)


0 Comments
Just comment your queries, we will reply as soon as possible.