ISC Biology Solved Paper 2023
ISC Class 12 Biology 2023 Question Paper Solution PDF is available here for free download. Use the Class 12 ISC Biology Paper 2023 answer key to give a boost to your exam preparation.
Evaluating previous year’s Class 12 ISC Biology Paper 2023 question paper solutions helps students get an idea about the difficulty level of the paper, exam pattern and the type of questions.
Previous year solved paper are proved to be very helpful for all students as it helps students to score good marks in board exams because they are board question papers and helps a lot of students who are going to appear in board examinations.
Also Read:
ISC Biology Paper 2023 Solutions
SECTION - A
(i) Name the source of thermostable DNA polymerase.
(i) Thermus aquaticus
(ii) Mention the scientific name of protozoan parasite that causes Amoebiasis.
(ii) Ascaris lumbricoides
(iii) What is cryopreservation?
(iii) Cryopreservation : It is the method of storage of materials at ultra-low temperature either by very rapid
cooling or by gradual cooling and simultaneous dehydration at low temperature.
(iv) The maternal grandfather of a boy is colour blind, but his maternal grandmother is normal. The father of the
boy is also normal. What is the probability of this boy being colour blind?
(iv) Data given: Maternal grandfather of a boy is colour blind. Therefore his daughter(Mother of boy) would
be carrier for colour blindness. Genotype would be xc
X on the other hand father of a boy is normal with
genotype (XY). So, boy has 50% probability of being colour blind.
(v) Name the type of antibody that can be transferred through the placenta.
(v) IgG is the antibody significantly transferred through the placenta.
(vi) During which phase of cell cycle, does DNA replication take place?
(vi) S- Phase of the interphase period in which DNA get doubled for cell division.
(vii) How many sets of primers are required in each cycle of PCR ?
(vii) Two sets of primers are required in each cycle of PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) . Primers are necessary to
start functioning of DNA polymerase.
(viii) Define perisperm.
(viii) The perisperm is the nucellus that remains after fertilisation. They are the nutritive tissues deposited external
to the embryo.e.g., Black pepper
(ix) Which one of the following enzymes is used to join DNA fragments?
(a) DNA polymerase
(b) Ligase
(c) Primase
(d) Endonuclease
(ix) Correct option is (b)
(x) What type of ecological pyramid would be obtained from the following data?
Secondary consumer: 120 gm
Primary consumer: 60 gm
Primary producer: 10 gm
(a) Inverted pyramid of biomass
(b) Pyramid of energy
(c) Upright pyramid of numbers
(d) Upright pyramid of biomass
(x) Correct option is (a)
(xi) Assertion: A person who has received a cut from a sharp object and is bleeding, needs to be given an anti-tetanus injection.
Reason: Anti-tetanus injection stimulates the production of antibodies for tetanus.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
(xi) Correct option is (c)
(xii) Which one of the following factors is responsible for activation of protoxin into active Bt toxin of Bacillus
thuringiensis ?
(a) Body temperature
(b) Moist surface of midgut
(c) Alkaline pH of gut
(d) Acidic pH of stomach
(xii) Correct option is (c)
(xiii) Give one significant contribution of each of the following scientists:
(a) T.R. Malthus
(b) R. Mishra
(xiii) (a) T.R. Malthus: He developed an exponential formula used to forecast population growth.
(b) R. Mishra: He contributed in the field of ecology, it refers to the relation and interaction between the
organism and their surrounding environment.
(xiv) Give a term for the following:
(a) An ART in which eggs are removed from the ovary of the female, fertilised and then placed in her
fallopian tube.
(b) Fusion of male gamete and secondary nucleus in angiosperms.
(xiv)
(a) IVF (in vitro fertilization ) and ZIFT (Zygote intra fallopian transfer)
(b) Triple fusion
(xv) Expand the following abbreviations:
(a) NACO
(b) PID
(xv)
(a) NACO: National Aids Control Organization
(b) PID: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
(xvi) Give a reason for each of the following:
(a) Cattle avoid browsing on Calotropis plant.
(b) DNA cannot enter directly into the host cell.
(xvi)
(a) Calotropis produces a milk like chemical toxin called cardiac glycosides that affect the heart hence cattle
avoid browsing on this plant.
(b) As DNA is a hydrophilic in nature and the cell membrane or plasma membrane is hydrophobic in nature
so this membrane do not allow DNA to enter in it.
SECTION - B
2. Give one difference between the following pairs:
(i) Sites of maturation of B - Lymphocytes and T – Lymphocytes
(ii) Sources of Opioids and Cannabinoids
2.
(i) B- lymphocytes matures in bone marrow while the T-lymphocytes matures in thymus gland.
(ii) Sources of- opioids is morphine which is extracted from the latex of poppy plant Papever somniferum,.
Cannabinoids are obtained from inflorescence of the plant Cannabis sativa.
3. Briefly discuss any two methods by which plants avoid self- pollination.
3. Self pollination can be prevented by-
(i) Dicliny or unisexuality- Both the male and female flowers are separate. E.g. Papaya
(ii) Dichogamy- Stigma and stamen matures at different times.
4. Mention the location and the function of Leydig cells.
4. Leydig cells are located in the testicles near the seminiferous tubules. They produces male sex hormone androgen
that helps in the production of secondary sexual characteristics of males after puberty.
5. (i) What are vestigial organs? Give any one example of a vestigial organ in human body.
5. Vestigial organs are the organs that do not have noticeable or apparent functions and counted as residual part of
the body . But our ancestors have the importance of that organ. e.g., Appendix, wisdom tooth, external ear, etc.
(ii) State Hardy Weinberg’s principle. Give a mathematical expression for this principle.
Hardy-Weinberg Principle : It says that allele frequencies in a population are stable and constant from generation
to generation. The gene pool (total genes and their alleles in a population) remains constant. This is called
genetic equilibrium (Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium). Sum total of all the allelic frequencies = 1
e.g., In a diploid, p and q are the frequencies of alleles A & a respectively.
The frequency of AA = p2 (i.e. the probability of an allele A with frequency p is the product of the probabilities,
i.e. p2 )
The frequency of aa = q2
The frequency of Aa = 2pq
Hence, p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 [binomial expansion of (p+q)
2 ]
6. Riya went to the hospital to meet her sister who was undergoing some treatment. The hospital was crowded with
patients suffering from various types of allergies, pneumonia and Ascariasis.
Name the disease that Riya is most likely to get infected with. Give one reason for your answer.
6. Riya is most likely to infected with pneumonia because it is a bacterial disease and spread through coughing
and sneezing, their bacteria are suspended in the air so the healthy person can be infected very easily. While in
allergies the contact with the infected person is necessary.
7. State the steps involved in the process of gene therapy for the treatment of ADA - deficiency
7. Gene therapy is a method of correcting defective gene that has been diagnosed in a child.
Steps involved in this therapy are:
(i) Lymphocytes of blood of the patient and grown in a culture medium outside the body.
(ii) A correct or functional ADA, cDNA is introduced into these lymphocytes and then again introduces into the
patient.
(iii) These cells are not immortal so the patient required periodic infusion of the same.
8. The pedigree chart given below represents the pattern of inheritance of sickle cell anaemia in a family. Study it
carefully and answer the questions that follow.
(i) What is the genotype of the father?
(ii) What is the phenotype of the mother?
8.
(i) Genotype of the father is HbA HbS (A carrier)
(ii) Phenotype of mother is diseased (Hbs Hbs
)
SECTION - C
9. Discuss any three major causes of loss of biodiversity.
9. Causes of loss of biodiversity:
(i) Over-exploitation: Biological processes are overexploited by man for the natural resources.
(ii) Habitat loss and fragmentation: Destruction of habitat cause extinction of many species. When large sized
habitat broken due to human settlement, buildings and roads, digging canals etc.
(iii) Alien species invasion: When alien species introduced unintentionally become invasive or harmful for the
indigenous species.
10.
(i) Name and describe the technique that helps in the separation and isolation of DNA fragments.
10. Gel electrophoresis is used in separation and isolation of the DNA fragments. It is a process of separation of
biomolecules by placing them in mild electric field.
(i) Fragments of DNA are separated by agarose gel electrophoresis.
(ii) DNA fragments being negatively charged move towards positive electrode/anode.
(iii) Fragments separate according to size/ charge.
(iv) Separated fragments are stained with ethidium bromide and exposed to UV rays and they form orange
coloured bands.
(ii) Study the diagram given below and answer .the questions that follow.
(a) Name the cloning vector shown above. In which organism is this cloning vector inserted?
(b) Mention any two restriction sites shown in the diagram.
(c) Name any two selectable markers shown in the diagram.
(a) Vector name is pBR322. The organism in which it is inserted is E.coli. bacteria.
(b) Two restriction sites are- Hind III and EcoR I.
(c) Two selectable markers are ampicillin and tetracycline.
11. Draw a neat and well labelled diagram of L. S of an anatropous ovule.
11. Diagram of an anatropous ovule is below:
12.
(i) Explain the process of sex - determination in grasshopper.
(ii) What is the genotype of Turner’s Syndrome? Mention any one symptom of this syndrome.
12.
(i) In grasshopper male have only one X chromosome besides autosomes and female have a pair of X
chromosomes.
(ii) Turner’s syndrome- Genotype are 44+XO i.e., have 45 chromosomes.
Symptoms- Sterile female with rudimentary ovaries.
13. With the help of neatly labelled diagrams, explain the different types of age pyramids of human population.
13. Age pyramid is a plot of the age distribution (per cent individuals of a given age or age group) for a population.
Age distribution depends upon the natality and mortality and determines the population growth. With regard to
age distribution, there are three kinds of population.
(i) Rapidly growing or expanding population: It has high birth rate and low death rate, so there are more
number of young individuals in the population. e.g.; India (young population).
(ii) Stationary or stable population: It has equal birth and death rates, so the population shows zero population
growth.
(iii) Declining population: It has higher death rate than birth rate, so the population of young members is
lower than that of old members, e.g., Japan (ageing population).
14. The scientists from a research institute collected samples of water from sewage pipes of two different cities, A,
and B. On analysis, the BOD value of the sample from city A was found to be 500 mg/L. The BOD value of the
sample from city B was 200 mg/L.
(i) Which one of the two cities needs a sewage treatment plant?
(ii) Briefly discuss the steps involved in the treatment of sewage.
(iii) What will be the effect of sewage treatment on the value of BOD?
14.
(a) City A needs a sewage treatment plant because its biological oxygen demand is high as comparative to city B.
(b) Steps involved in the sewage treatment are as follows-
Municipal wastewater (sewage) contains large amount of organic matter and microbes which are pathogenic
and cannot be discharged into natural water bodies like rivers and streams.
Sewage is treated in sewage treatment plant to make it less polluting by using heterotrophic microbes
naturally present in sewage.
Sewage treatment is done in two stages:
Primary treatment: In primary treatment, floating debris is removed by sequential filtration. Grit (soil and
small pebbles) are removed by sedimentation.
Secondary treatment: Secondary treatment or biological treatment involves passing of primary effluents
in large aeration tank to help the growth of aerobic microbes into flocs (masses of bacteria associated with
fungal filaments to form mesh like structures). These microbes increase the consumption of organic wastes
and decrease the BOD (biological oxygen demand) of the effluents.
(c) After proper sewage treatment the value of BOD will decreases useful microbes consume lot of organic
matter.
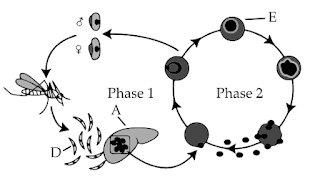
15. The diagram given below shows the life cycle of a malarial Parasite. Study it carefully and answer the questions
that follow:
(i) Name the hosts in which the asexual phase and sexual phase of the life cycle take place.
(ii) Identify the infective stage labelled ‘D’.
(iii) Name the structures labelled ‘A’ and ‘E’
(iv) Give any one symptom of malaria.
15.
(i) As it is a plasmodium a malarial parasite which completed its life cycle in two hosts- asexual phase in human
host and sexual phase in female Anopheles mosquito host.
(ii) label D shows- sporozoites.
(iii) Label A and E shows- liver cells and trophozoites respectively.
(iv) Signs and symptoms of malaria are- fever, chills, abdominal pain, general feeling of discomfort, etc.
SECTION - D
16. Explain the components of the structural genes in the Lac operon system in E. coli. How does the operon function
in the presence of lactose?
16. There are three structural genes (z, y, a) which transcribe a polycistronic mRNA.
(i) Gene z codes for b-galactosidase (b-gal), which catalyses the hydrolysis of lactose into galactose and glucose.
(ii) Gene y codes for permease, which increases the permeability of the cell to b-galactosidase (lactose).
(iii) Gene a codes for transacetylase, which catalyses the transacetylation of lactose into its active form.
17.
(i) Given below is the diagram depicting the menstrual cycle in human beings. Study it carefully and answer
the questions that follow.
(a) Which phases are indicated by ‘C and ‘D’?
(b) Name the structure labelled ‘F’? What is its role?
(c) Explain the changes in the level of progesterone during phases ‘C’ and ‘D’.
(d) Which hormone present in the urine confirms pregnancy in human beings?
(e) Identify the structure labelled ‘E’. Name the hormone released by it.
17.
(i) In the given diagram ‘C’ indicates luteal phase and ‘D’ indicates the next menstrual cycle begins.
(ii) ‘F’- Corpus luteum
(iii) During luteal phase the progesterone level increases which thickens the uterus lining for implantation of
fertilized egg. If the egg is not fertilised the progesterone level decreases and the female get there periods.
(iv) Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) hormone present in the urine that confirms the pregnancy in
humans.
(v) ‘E’- Graffian Follicles which releases progesterone hormone.
(ii) According to a survey conducted by the Government of India in the year 1950,the population of the country
was 350 million. In the next survey conducted in the year 2010, die population had reached above 1000
million.
(a) List any two reasons for this rise in the population.
(b) Suggest any two steps which should be taken by the Government to control this rise.
(c) How does the population explosion affect the growth of a country?
(d) What is the difference between the natural and artificial contraceptive methods? Give one example of each
method.
(ii)
(a) Reasons for high population growth:
• Rapid decline in death rate to better public health care.
• Decline in maternal and infant mortality rates.
(b) Steps taken by the government to control the population are:
• Family planning programs were initiated by the Government of India.
• Encouraging sex education the schools to give the right information to the young people.
(c) The rapid growing population of our country transforms the economy into mass unemployment where
the situation getting uncontrolled due to lack of resources over population.
(d) Natural Methods: They work on the principle of avoiding chances of ovum and sperms meeting. It
includes:
• Periodic abstinence: It is a method in which the couples avoid or abstain from coitus from day 10 to 17 of
the menstrual cycle when ovulation could be expected, as chances of fertilization are very high during
this period. It is called the fertile period.
• Withdrawal or coitus interruptus: It is another method in which the male partner withdraws his penis
from the vagina just before ejaculation so as to avoid insemination.
• Lactational amenorrhea: It is a method which is based on the fact that ovulation and therefore the cycle
do not occur during the period of intense lactation following parturition.
• Artificial Methods: This involves mechanical or barrier methods. In barrier methods, ovum and sperms
are prevented from physically meeting with the help of barriers. These methods are available for both
males and females. It includes:
• Condoms
• Diaphragms, Cervical caps and Vaults
• Spermicidal creams, jellies
18. Describe the mechanism of decomposition by explaining the various processes involved in it.
18. Decomposition : It is the breakdown of complex organic matter by decomposers into inorganic substances like
carbon dioxide, water and nutrients.
• The detritus is the raw material for decomposition. Detritus are dead plant remains such as leaves, bark,
flowers and dead remains of animals, including faecal matter.
• The earthworm is referred to as the ‘farmer’s friend’. This is so because they help in the breakdown of
complex organic matter as well as in loosening of the soil.
• The steps involved in the decomposition process are :
(a) Fragmentation: It is the breakdown of detritus into smaller particles by detritivores like earthworm
(b) Leaching: Here, the water soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated
as unavailable salts.
(c) Catabolism: It is the degradation of detritus into simpler inorganic substances by bacterial and fungal
enzymes.
(d) Humification: The degradation of detritus leads to accumulation of humus, a dark amorphous
substance in soil. Humus is resistant to microbial action and so decomposes very slowly. Being colloidal
in nature, it serves as a reservoir of nutrients.
(e) Mineralization: The humus gets degraded by some microbes and release inorganic nutrients. This
process is called mineralization.
(f) Nutrient immobilization: At times, the soil nutrients instead of getting mineralized, get bound with
biomass of microbes, and so become temporarily unavailable to other organisms. This incorporation of
nutrients in living microbes is called nutrient immobilization.

















.png)

0 Comments
Just comment your queries, we will reply as soon as possible.